E'kabel Blog
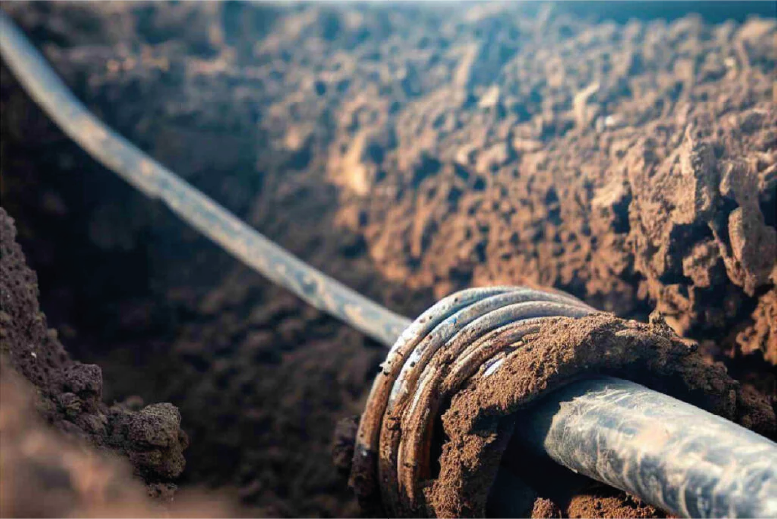
Cables directly buried
How to reduce the carbon footprint with direct burial cables
The essence of a photovoltaic park is to generate clean energy. Therefore logical that environmental criteria should guide decisions at all stages of its planning and construction. Although wires may seem like a passive element in these installations, its correct selection determines whether the total CO2 emissions associated with the project increase or decrease.
There are various approaches to installing electrical wiring. The main methods include overhead and underground installations. The choice between these methods depends on factors such as load distribution, distance between connection points, design optimization, and cost reduction.
Both approaches are common, but overhead installation methods are more frequent due to their construction nature. On the other hand, underground methods are used in various residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Solar farms require extensive wiring installations, and the underground method offers the advantage of low maintenance. Underground wiring can be installed using: pipes, concrete ducts, or direct burial.
Direct burial gains popularity
The use of direct burial as a cable installation technique is not new, but with the constant growth of the solar photovoltaic industry, it has become the preferred installation method. Because it avoids the use of concrete ducts.
The use of cement brings benefits: for every 1000 grams of cement produced, about 900 grams of CO2 are generated. Additionally, the cement industry is responsible for around 8% of global CO2 emissions, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Cement production has also been associated with water contamination. Chemicals such as calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide are used in the production of this material, which, if improperly discharged into water bodies, are harmful to marine ecosystems.
Additionally, the extraction of raw materials for cement production, such as sand, gravel, and limestone, can cause the destruction of natural habitats and the consequent displacement of wildlife. Cement, being a non-biodegradable material, does not degrade naturally in the environment and is the main contributor to the urban heat island effect, which raises temperatures in urban areas.
Direct burial gains popularity
The use of direct burial as a cable installation technique is not new, but with the constant growth of the solar photovoltaic industry, it has become the preferred installation method. Because it avoids the use of concrete ducts.
The use of cement brings benefits: for every 1000 grams of cement produced, about 900 grams of CO2 are generated. Additionally, the cement industry is responsible for around 8% of global CO2 emissions, according to the International Energy Agency (IEA).
Cement production has also been associated with water contamination. Chemicals such as calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide are used in the production of this material, which, if improperly discharged into water bodies, are harmful to marine ecosystems.
Additionally, the extraction of raw materials for cement production, such as sand, gravel, and limestone, can cause the destruction of natural habitats and the consequent displacement of wildlife. Cement, being a non-biodegradable material, does not degrade naturally in the environment and is the main contributor to the urban heat island effect, which raises temperatures in urban areas.
A compelling example
To perform an underground installation of 1000 meters in length through a concrete duct, the following are required:
- 70,000 liters of water
- 260m³ of cement
That is are enough to supply water to seven households for approximately one month and to build 26 houses of 100m².
It is common in solar parks to find underground cables that are longer than 1000 meters, which increases the use of cement and water needed for the installation if concrete ducts are chosen.
Switching from concrete duct methods to direct burial for cabling reduces water and cement consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. The application of the direct burial technique does not require cement, making it an environmentally friendly approach.
Requirements for using direct burial cables
Cables designated for direct burial have different requirements depending on their voltage insulation level. For low-voltage control and power cables, it is advisable to consult the UL-1277 standard, and for medium-voltage power cables, the UL-1072 standard is recommended. By meeting these requirements, the cable obtains the UL Listed certification for direct burial.
“There are different approaches to installing electrical wiring. Notable methods include aerial installation and underground installation.”
Author:
Electrical Engineer, graduated from Simón Bolívar University, Caracas – Venezuela. She has studied logistics and international trade. Her experience began with the planning and optimization of energy consumption projects at Nestlé. She currently works at E’kabel, analyzing and developing energy transport solutions for companies in the Oil & Gas, Mining, and Renewable Energy sectors in the international market.